1 //! [![github]](https://github.com/dtolnay/itoa) [![crates-io]](https://crates.io/crates/itoa) [![docs-rs]](https://docs.rs/itoa) 2 //! 3 //! [github]: https://img.shields.io/badge/github-8da0cb?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=github 4 //! [crates-io]: https://img.shields.io/badge/crates.io-fc8d62?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=rust 5 //! [docs-rs]: https://img.shields.io/badge/docs.rs-66c2a5?style=for-the-badge&labelColor=555555&logo=docs.rs 6 //! 7 //! <br> 8 //! 9 //! This crate provides a fast conversion of integer primitives to decimal 10 //! strings. The implementation comes straight from [libcore] but avoids the 11 //! performance penalty of going through [`core::fmt::Formatter`]. 12 //! 13 //! See also [`ryu`] for printing floating point primitives. 14 //! 15 //! [libcore]: https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/b8214dc6c6fc20d0a660fb5700dca9ebf51ebe89/src/libcore/fmt/num.rs#L201-L254 16 //! [`core::fmt::Formatter`]: https://doc.rust-lang.org/std/fmt/struct.Formatter.html 17 //! [`ryu`]: https://github.com/dtolnay/ryu 18 //! 19 //! # Example 20 //! 21 //! ``` 22 //! fn main() { 23 //! let mut buffer = itoa::Buffer::new(); 24 //! let printed = buffer.format(128u64); 25 //! assert_eq!(printed, "128"); 26 //! } 27 //! ``` 28 //! 29 //! # Performance (lower is better) 30 //! 31 //! 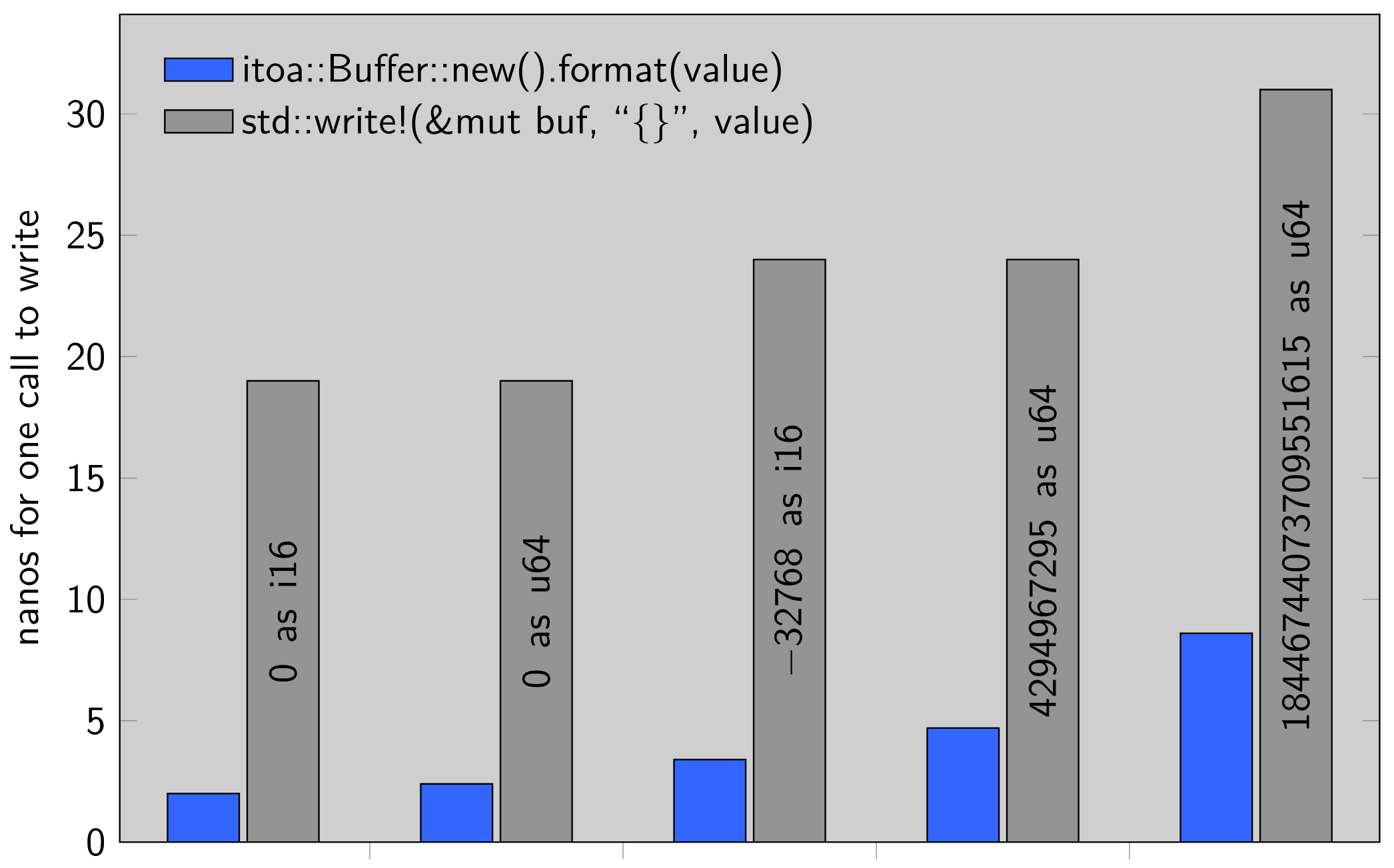 32 33 #![doc(html_root_url = "https://docs.rs/itoa/1.0.10")] 34 #![no_std] 35 #![allow( 36 clippy::cast_lossless, 37 clippy::cast_possible_truncation, 38 clippy::expl_impl_clone_on_copy, 39 clippy::must_use_candidate, 40 clippy::needless_doctest_main, 41 clippy::unreadable_literal 42 )] 43 44 mod udiv128; 45 46 use core::mem::{self, MaybeUninit}; 47 use core::{ptr, slice, str}; 48 #[cfg(feature = "no-panic")] 49 use no_panic::no_panic; 50 51 /// Local Android change: Use std to allow building as a dylib. 52 #[cfg(android_dylib)] 53 extern crate std; 54 55 /// A correctly sized stack allocation for the formatted integer to be written 56 /// into. 57 /// 58 /// # Example 59 /// 60 /// ``` 61 /// let mut buffer = itoa::Buffer::new(); 62 /// let printed = buffer.format(1234); 63 /// assert_eq!(printed, "1234"); 64 /// ``` 65 pub struct Buffer { 66 bytes: [MaybeUninit<u8>; I128_MAX_LEN], 67 } 68 69 impl Default for Buffer { 70 #[inline] default() -> Buffer71 fn default() -> Buffer { 72 Buffer::new() 73 } 74 } 75 76 impl Copy for Buffer {} 77 78 impl Clone for Buffer { 79 #[inline] 80 #[allow(clippy::non_canonical_clone_impl)] // false positive https://github.com/rust-lang/rust-clippy/issues/11072 clone(&self) -> Self81 fn clone(&self) -> Self { 82 Buffer::new() 83 } 84 } 85 86 impl Buffer { 87 /// This is a cheap operation; you don't need to worry about reusing buffers 88 /// for efficiency. 89 #[inline] 90 #[cfg_attr(feature = "no-panic", no_panic)] new() -> Buffer91 pub fn new() -> Buffer { 92 let bytes = [MaybeUninit::<u8>::uninit(); I128_MAX_LEN]; 93 Buffer { bytes } 94 } 95 96 /// Print an integer into this buffer and return a reference to its string 97 /// representation within the buffer. 98 #[cfg_attr(feature = "no-panic", no_panic)] format<I: Integer>(&mut self, i: I) -> &str99 pub fn format<I: Integer>(&mut self, i: I) -> &str { 100 i.write(unsafe { 101 &mut *(&mut self.bytes as *mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; I128_MAX_LEN] 102 as *mut <I as private::Sealed>::Buffer) 103 }) 104 } 105 } 106 107 /// An integer that can be written into an [`itoa::Buffer`][Buffer]. 108 /// 109 /// This trait is sealed and cannot be implemented for types outside of itoa. 110 pub trait Integer: private::Sealed {} 111 112 // Seal to prevent downstream implementations of the Integer trait. 113 mod private { 114 pub trait Sealed: Copy { 115 type Buffer: 'static; write(self, buf: &mut Self::Buffer) -> &str116 fn write(self, buf: &mut Self::Buffer) -> &str; 117 } 118 } 119 120 const DEC_DIGITS_LUT: &[u8] = b"\ 121 0001020304050607080910111213141516171819\ 122 2021222324252627282930313233343536373839\ 123 4041424344454647484950515253545556575859\ 124 6061626364656667686970717273747576777879\ 125 8081828384858687888990919293949596979899"; 126 127 // Adaptation of the original implementation at 128 // https://github.com/rust-lang/rust/blob/b8214dc6c6fc20d0a660fb5700dca9ebf51ebe89/src/libcore/fmt/num.rs#L188-L266 129 macro_rules! impl_Integer { 130 ($($max_len:expr => $t:ident),* as $conv_fn:ident) => {$( 131 impl Integer for $t {} 132 133 impl private::Sealed for $t { 134 type Buffer = [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len]; 135 136 #[allow(unused_comparisons)] 137 #[inline] 138 #[cfg_attr(feature = "no-panic", no_panic)] 139 fn write(self, buf: &mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len]) -> &str { 140 let is_nonnegative = self >= 0; 141 let mut n = if is_nonnegative { 142 self as $conv_fn 143 } else { 144 // convert the negative num to positive by summing 1 to it's 2 complement 145 (!(self as $conv_fn)).wrapping_add(1) 146 }; 147 let mut curr = buf.len() as isize; 148 let buf_ptr = buf.as_mut_ptr() as *mut u8; 149 let lut_ptr = DEC_DIGITS_LUT.as_ptr(); 150 151 unsafe { 152 // need at least 16 bits for the 4-characters-at-a-time to work. 153 if mem::size_of::<$t>() >= 2 { 154 // eagerly decode 4 characters at a time 155 while n >= 10000 { 156 let rem = (n % 10000) as isize; 157 n /= 10000; 158 159 let d1 = (rem / 100) << 1; 160 let d2 = (rem % 100) << 1; 161 curr -= 4; 162 ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d1), buf_ptr.offset(curr), 2); 163 ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d2), buf_ptr.offset(curr + 2), 2); 164 } 165 } 166 167 // if we reach here numbers are <= 9999, so at most 4 chars long 168 let mut n = n as isize; // possibly reduce 64bit math 169 170 // decode 2 more chars, if > 2 chars 171 if n >= 100 { 172 let d1 = (n % 100) << 1; 173 n /= 100; 174 curr -= 2; 175 ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d1), buf_ptr.offset(curr), 2); 176 } 177 178 // decode last 1 or 2 chars 179 if n < 10 { 180 curr -= 1; 181 *buf_ptr.offset(curr) = (n as u8) + b'0'; 182 } else { 183 let d1 = n << 1; 184 curr -= 2; 185 ptr::copy_nonoverlapping(lut_ptr.offset(d1), buf_ptr.offset(curr), 2); 186 } 187 188 if !is_nonnegative { 189 curr -= 1; 190 *buf_ptr.offset(curr) = b'-'; 191 } 192 } 193 194 let len = buf.len() - curr as usize; 195 let bytes = unsafe { slice::from_raw_parts(buf_ptr.offset(curr), len) }; 196 unsafe { str::from_utf8_unchecked(bytes) } 197 } 198 } 199 )*}; 200 } 201 202 const I8_MAX_LEN: usize = 4; 203 const U8_MAX_LEN: usize = 3; 204 const I16_MAX_LEN: usize = 6; 205 const U16_MAX_LEN: usize = 5; 206 const I32_MAX_LEN: usize = 11; 207 const U32_MAX_LEN: usize = 10; 208 const I64_MAX_LEN: usize = 20; 209 const U64_MAX_LEN: usize = 20; 210 211 impl_Integer!( 212 I8_MAX_LEN => i8, 213 U8_MAX_LEN => u8, 214 I16_MAX_LEN => i16, 215 U16_MAX_LEN => u16, 216 I32_MAX_LEN => i32, 217 U32_MAX_LEN => u32 218 as u32); 219 220 impl_Integer!(I64_MAX_LEN => i64, U64_MAX_LEN => u64 as u64); 221 222 #[cfg(target_pointer_width = "16")] 223 impl_Integer!(I16_MAX_LEN => isize, U16_MAX_LEN => usize as u16); 224 225 #[cfg(target_pointer_width = "32")] 226 impl_Integer!(I32_MAX_LEN => isize, U32_MAX_LEN => usize as u32); 227 228 #[cfg(target_pointer_width = "64")] 229 impl_Integer!(I64_MAX_LEN => isize, U64_MAX_LEN => usize as u64); 230 231 macro_rules! impl_Integer128 { 232 ($($max_len:expr => $t:ident),*) => {$( 233 impl Integer for $t {} 234 235 impl private::Sealed for $t { 236 type Buffer = [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len]; 237 238 #[allow(unused_comparisons)] 239 #[inline] 240 #[cfg_attr(feature = "no-panic", no_panic)] 241 fn write(self, buf: &mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; $max_len]) -> &str { 242 let is_nonnegative = self >= 0; 243 let n = if is_nonnegative { 244 self as u128 245 } else { 246 // convert the negative num to positive by summing 1 to it's 2 complement 247 (!(self as u128)).wrapping_add(1) 248 }; 249 let mut curr = buf.len() as isize; 250 let buf_ptr = buf.as_mut_ptr() as *mut u8; 251 252 unsafe { 253 // Divide by 10^19 which is the highest power less than 2^64. 254 let (n, rem) = udiv128::udivmod_1e19(n); 255 let buf1 = buf_ptr.offset(curr - U64_MAX_LEN as isize) as *mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; U64_MAX_LEN]; 256 curr -= rem.write(&mut *buf1).len() as isize; 257 258 if n != 0 { 259 // Memset the base10 leading zeros of rem. 260 let target = buf.len() as isize - 19; 261 ptr::write_bytes(buf_ptr.offset(target), b'0', (curr - target) as usize); 262 curr = target; 263 264 // Divide by 10^19 again. 265 let (n, rem) = udiv128::udivmod_1e19(n); 266 let buf2 = buf_ptr.offset(curr - U64_MAX_LEN as isize) as *mut [MaybeUninit<u8>; U64_MAX_LEN]; 267 curr -= rem.write(&mut *buf2).len() as isize; 268 269 if n != 0 { 270 // Memset the leading zeros. 271 let target = buf.len() as isize - 38; 272 ptr::write_bytes(buf_ptr.offset(target), b'0', (curr - target) as usize); 273 curr = target; 274 275 // There is at most one digit left 276 // because u128::max / 10^19 / 10^19 is 3. 277 curr -= 1; 278 *buf_ptr.offset(curr) = (n as u8) + b'0'; 279 } 280 } 281 282 if !is_nonnegative { 283 curr -= 1; 284 *buf_ptr.offset(curr) = b'-'; 285 } 286 287 let len = buf.len() - curr as usize; 288 let bytes = slice::from_raw_parts(buf_ptr.offset(curr), len); 289 str::from_utf8_unchecked(bytes) 290 } 291 } 292 } 293 )*}; 294 } 295 296 const U128_MAX_LEN: usize = 39; 297 const I128_MAX_LEN: usize = 40; 298 299 impl_Integer128!(I128_MAX_LEN => i128, U128_MAX_LEN => u128); 300